conditions
Arrhythmias
A healthy heart has a healthy rhythm. If you feel your heart is beating too fast or too slow, or if your heartbeats seem irregular, that could be a sign of an arrhythmia.
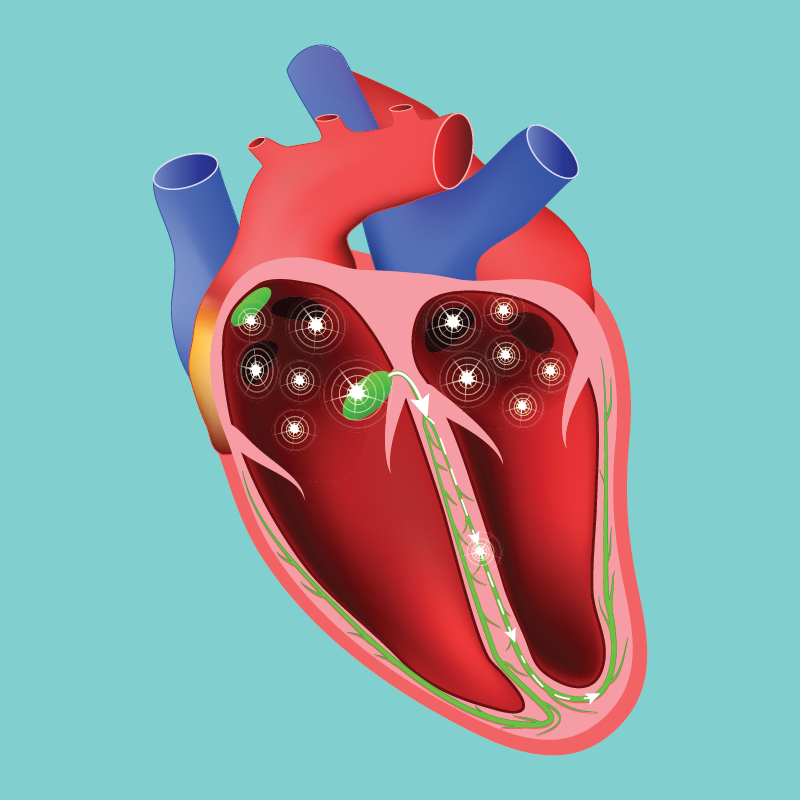
Abnormal contractions of the heart are called arrhythmias. An arrhythmia can cause dizziness, light-headedness, palpitations (the sensation that your heart is beating too fast or skipping a beat), or the feeling that you might pass out.
Despite these uncomfortable sensations, many cases of arrhythmia are actually benign. However, some arrhythmias, especially if they are accompanied by additional symptoms, can indicate serious cardiovascular issues.
There are two main types of arrhythmias: tachycardias and bradycardias. Each has its own set of symptoms and associated concerns. Tachycardias cause resting heart rates that are faster than normal. Atrial fibrillation, an abnormal heart rhythm involving the upper (atrial) chambers of the heart, is an example of tachycardia. Bradycardias cause resting heart rates that are slower than normal. Depending on the circumstances, a heart rate that’s too slow can be just as dangerous as one that’s too fast.
If you experience an irregular heartbeat that’s accompanied by sweating, fainting, anxiety, fatigue, chest pain, or shortness of breath, you should seek medical attention immediately.
Arrhythmias may occur as a result of underlying cardiovascular disease, genetic syndromes, or certain lifestyle factors. Diabetes, sleep apnea, hypertension, thyroid problems, obesity, and coronary disease all increase the risk of developing an arrhythmia.
Understanding what type of arrhythmia you have is essential to determining the right treatment plan. If you experience palpitations, dizziness, lightheadedness, or the feeling that you might pass out, contact Manhattan Cardiovascular Associates for an evaluation. Our specialists can draw from a range of diagnostic tests to evaluate your heart health, including electrocardiograms, echocardiograms, and wearable heart monitors.
Bradycardias are sometimes treated by implanting a pacemaker, which will stimulate your heart to beat if it slows or stops. Tachycardias can be treated with medication or by means of various medical procedures. If the tests determine that your arrhythmia is benign, your doctor may recommend only lifestyle changes.
No matter what kind of arrhythmia you have, the doctors at Manhattan Cardiovascular Associates can create a plan to prevent recurrences. Many arrhythmias can be prevented by treating underlying cardiac conditions, managing any other health issues, and implementing simple lifestyle changes.

